End Effectors
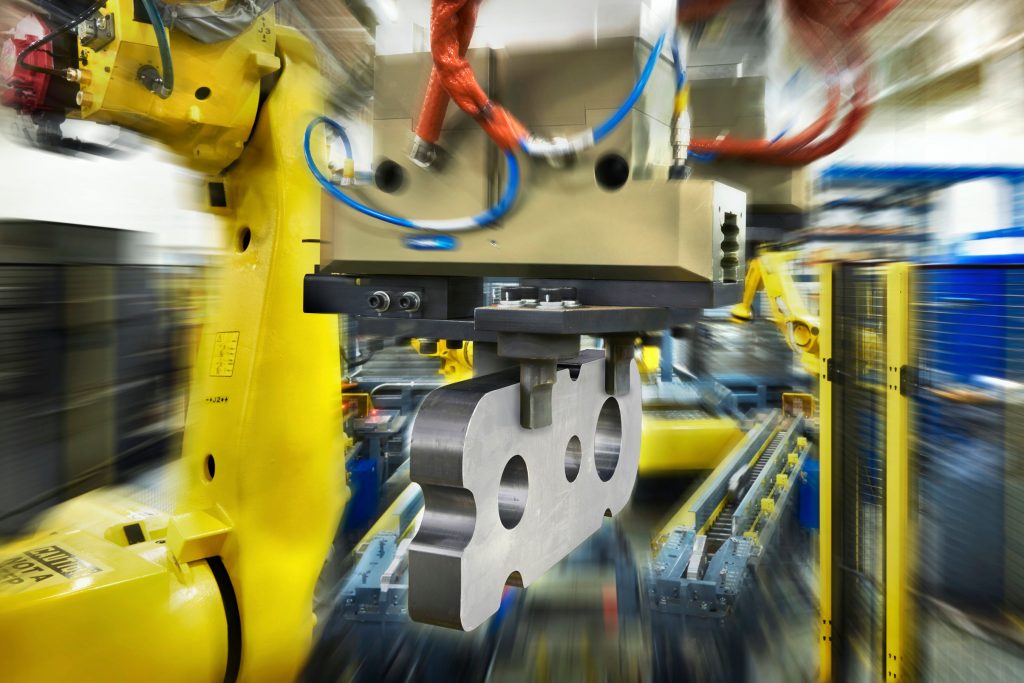

Robots are nothing without their tools
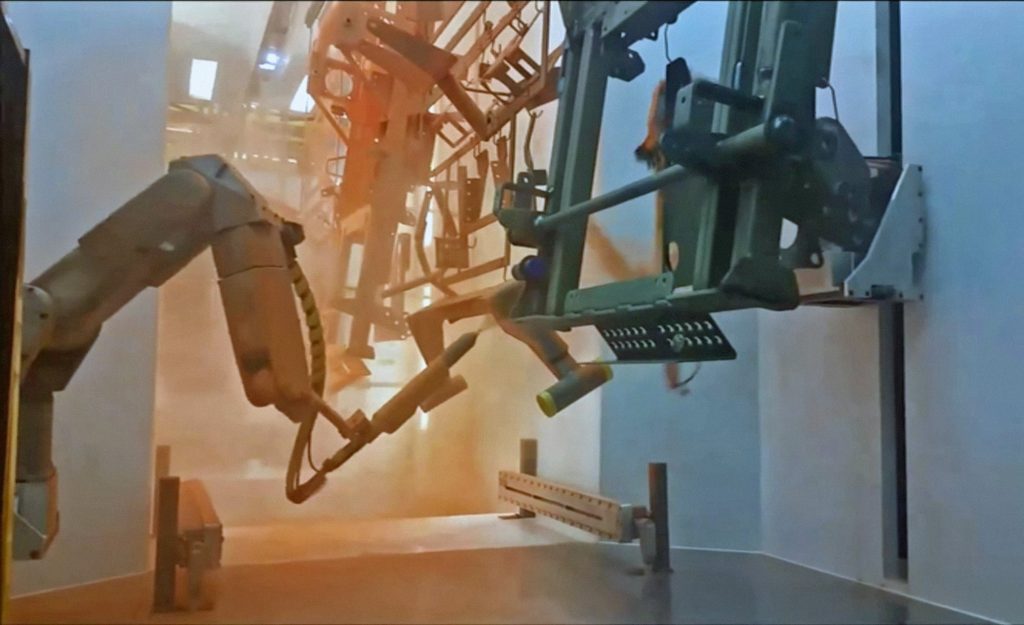
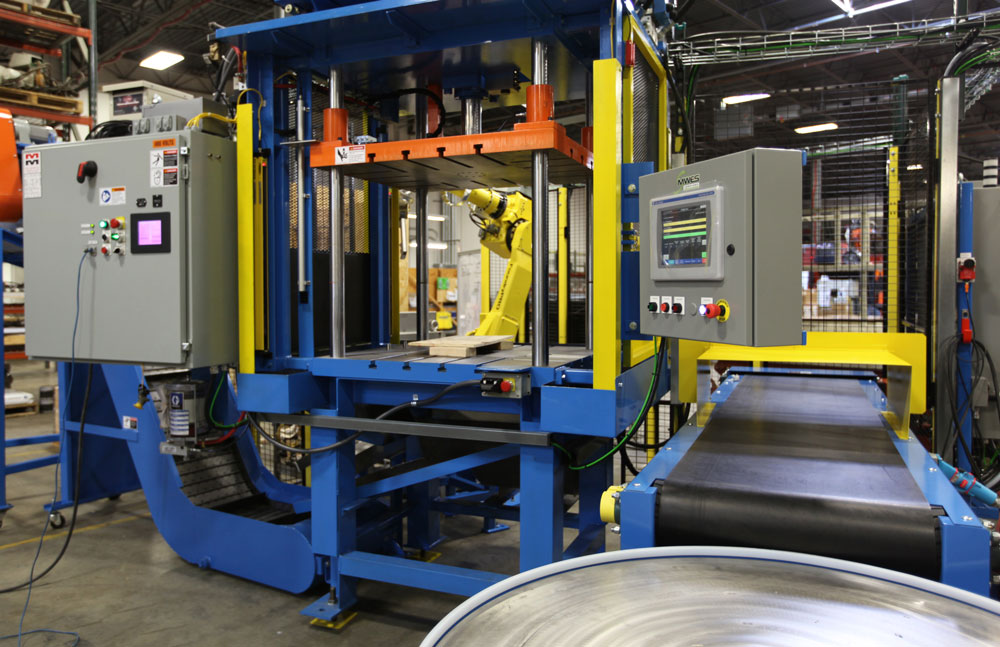
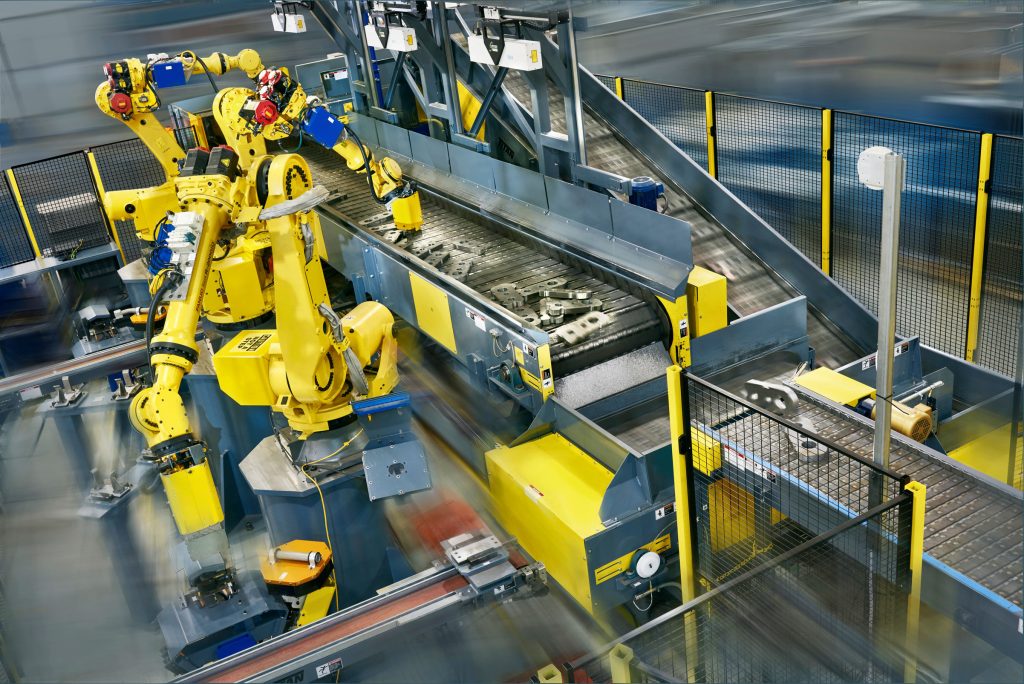
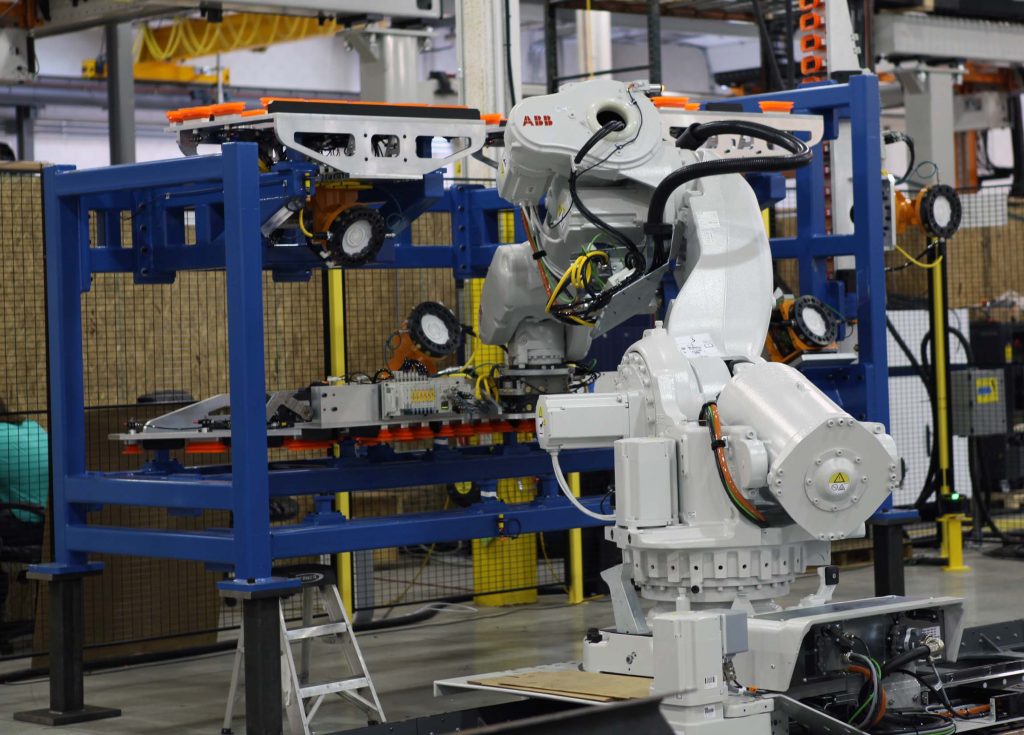
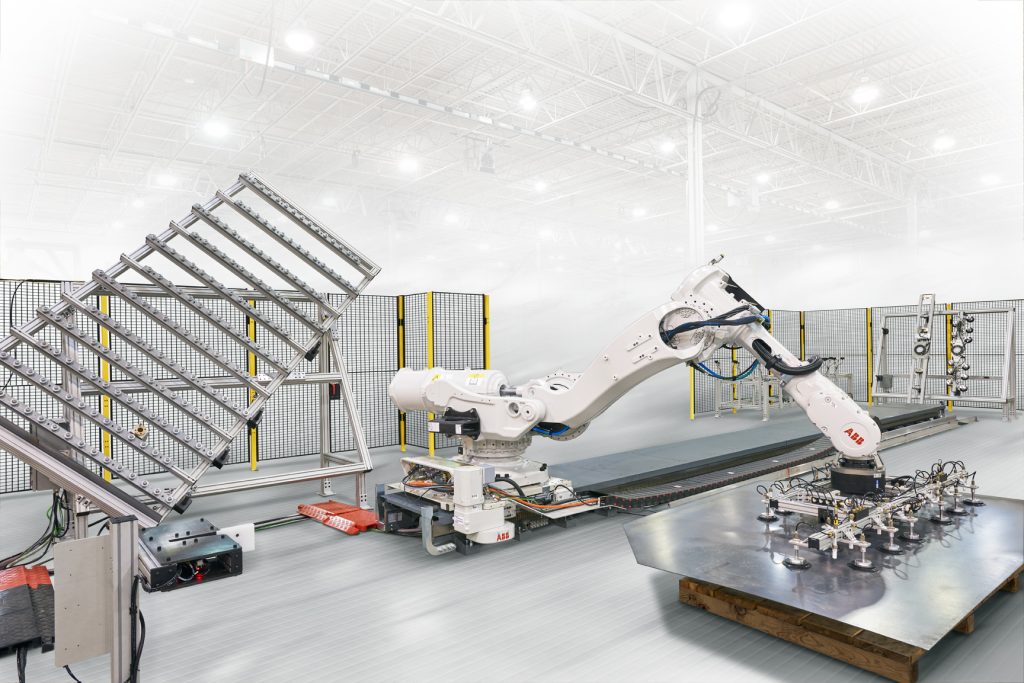
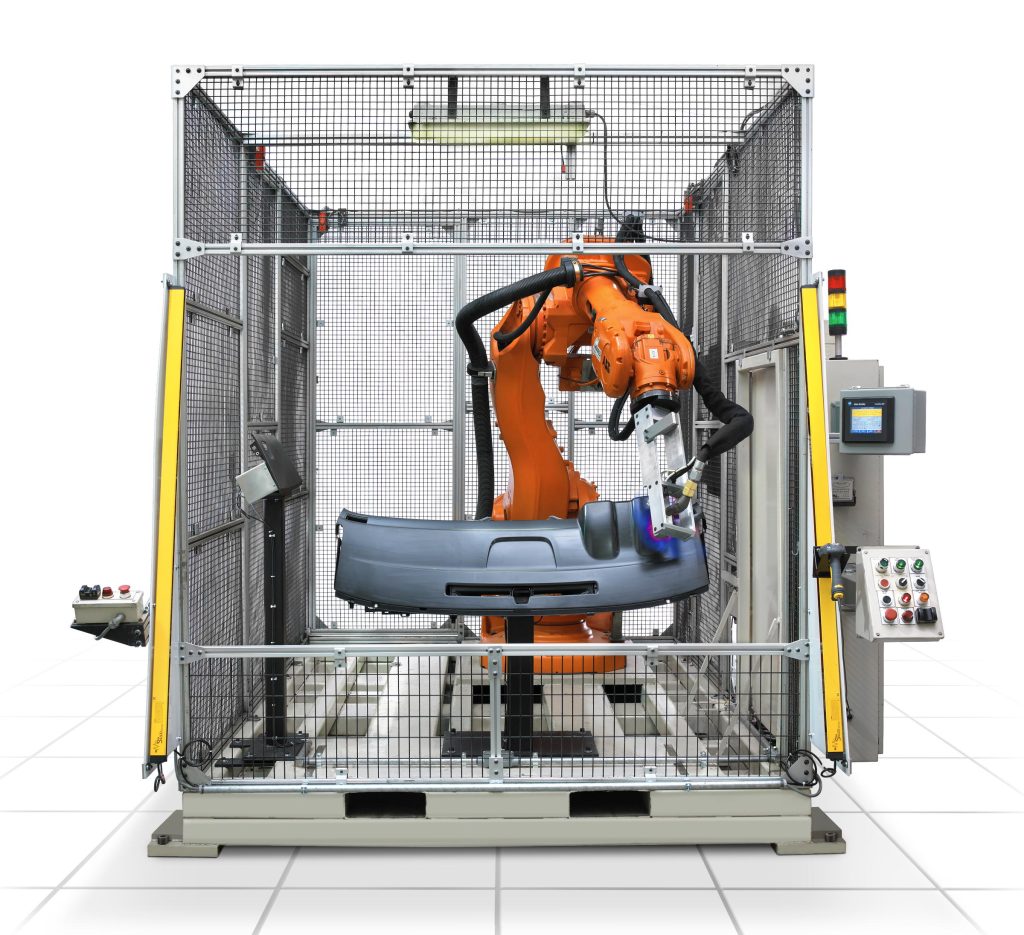
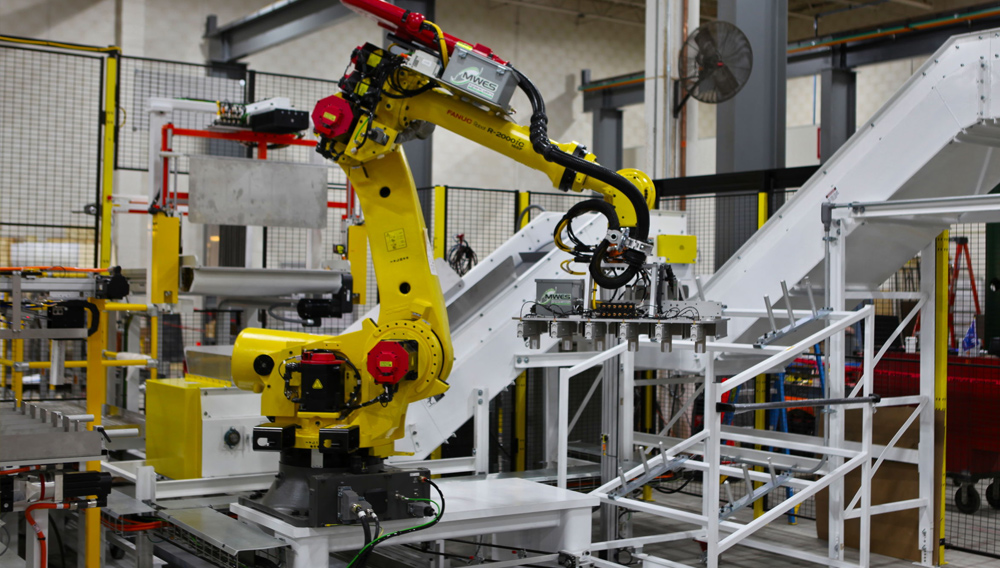
End effectors, also commonly known as End-Of-Arm-Tool (EOAT), are the hands of a robot arm and as such a critical component that directly interacts with the environment. End effectors can be made up of a combination of grippers, collision sensors, force-torque sensors, vision systems and custom material processing tools. Additionally, tool changers are another common feature of an end effector. Tool changers allow the robot to quickly switch out its EOAT autonomously without operator intervention. The options and interchangeability are endless with all the tooling currently available.
Since they are simple to install and offer a lot of power in a tiny container, pneumatic EOATs have proven to be the most common solution for material handling robots. Since pick-and-place tasks are excellent candidates for automation and robots’ grasping abilities have improved dramatically in recent years.
Common Types of End Effectors
Robots perform tasks precisely and consistently, but their effectiveness depends on the tools attached to their arms. There are several common types of robots with each type suited for a different application and EOAT attachment.
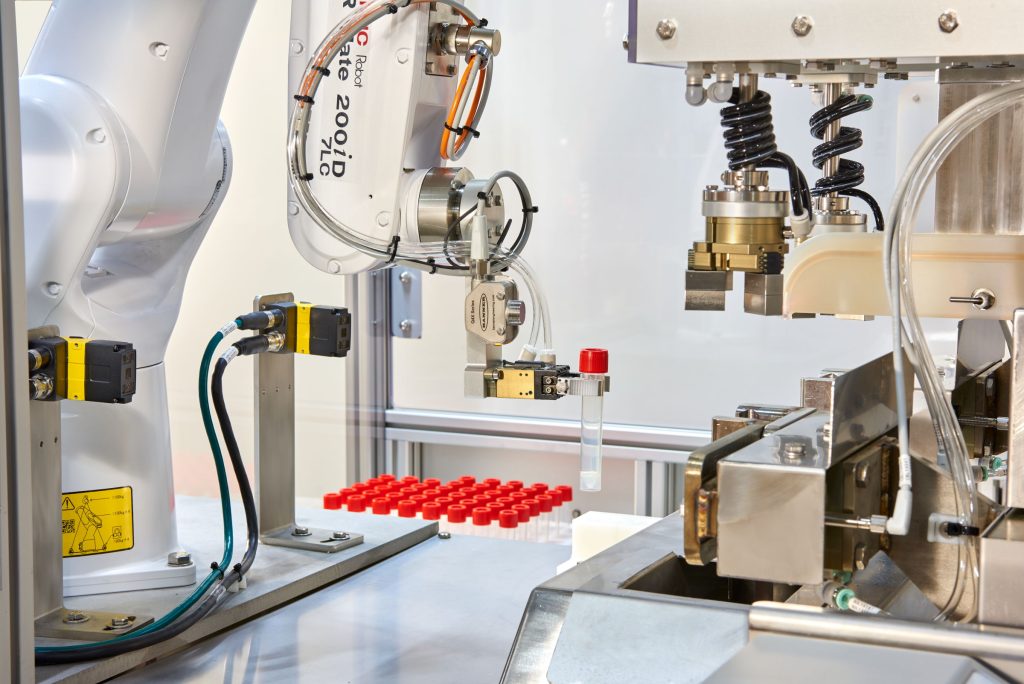
- Grippers – These are versatile tools that grasp, hold, and manipulate objects. They can be pneumatic, electric or vacuum-based. Grippers vary in design, including parallel-jaw, three-finger and soft grippers.
- Vacuum Tools – Ideal for handling flat or porous objects, vacuum tools use suction to lift and move items. Vacuum EOATs are common in packaging, palletizing, general material handling, glass pane handling and electronics assembly.
- Welding Tools – EOATs equipped with welding torches perform automated welding tasks. They ensure precise positioning and consistent weld quality.
- Screwdrivers and Nutrunners – For assembly tasks, robots use EOATs with built-in screwdrivers or Nutrunners. These tools tighten screws and bolts efficiently.
- Spray Guns – In painting or coating applications, robots equipped with spray guns ensure uniform coverage and reduce overspray.
- Grinding Tools – Grinders, sanders and other material removal EOATs are commonly used with robot systems.
Recent advancements include collaborative EOATs that allow humans and robots to work together safely. These tools sense human presence and adjust their force accordingly. Additionally, EOATs with adaptive compliance improve the handling of irregularly shaped objects. As automation continues to evolve, so will these essential tools, enabling robots to perform an ever-widening range of tasks.
The future of Robotic Automation
Robotic automation is rapidly becoming a crucial component of an already evolving world. The automation products Midwest Engineered Systems provides can elevate your business to new heights. Contact us today if your business is looking to expand its production capacity or to move away from the rigors of a manual labor workforce.
Building the future of manufacturing, together
World-class Automation