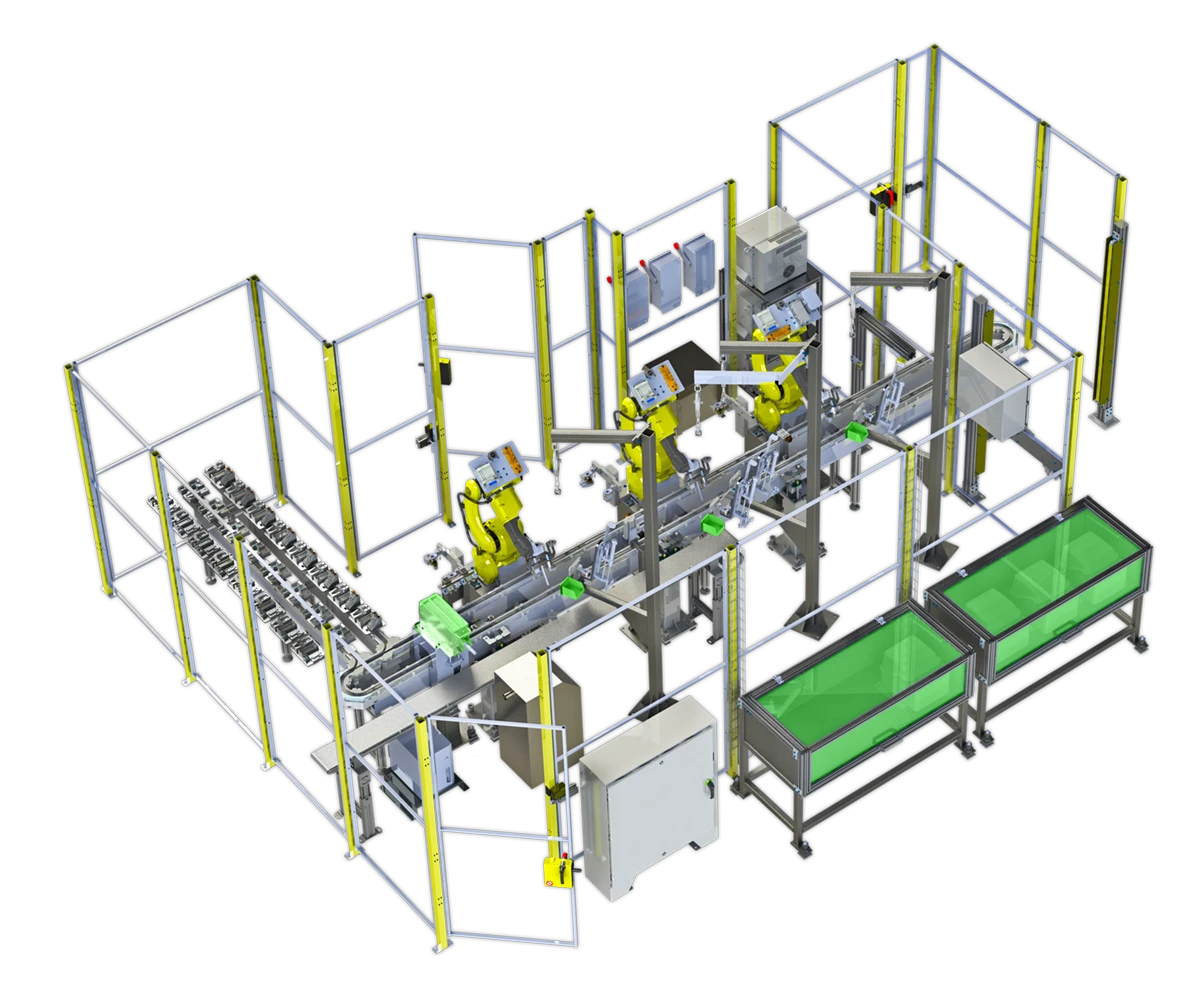
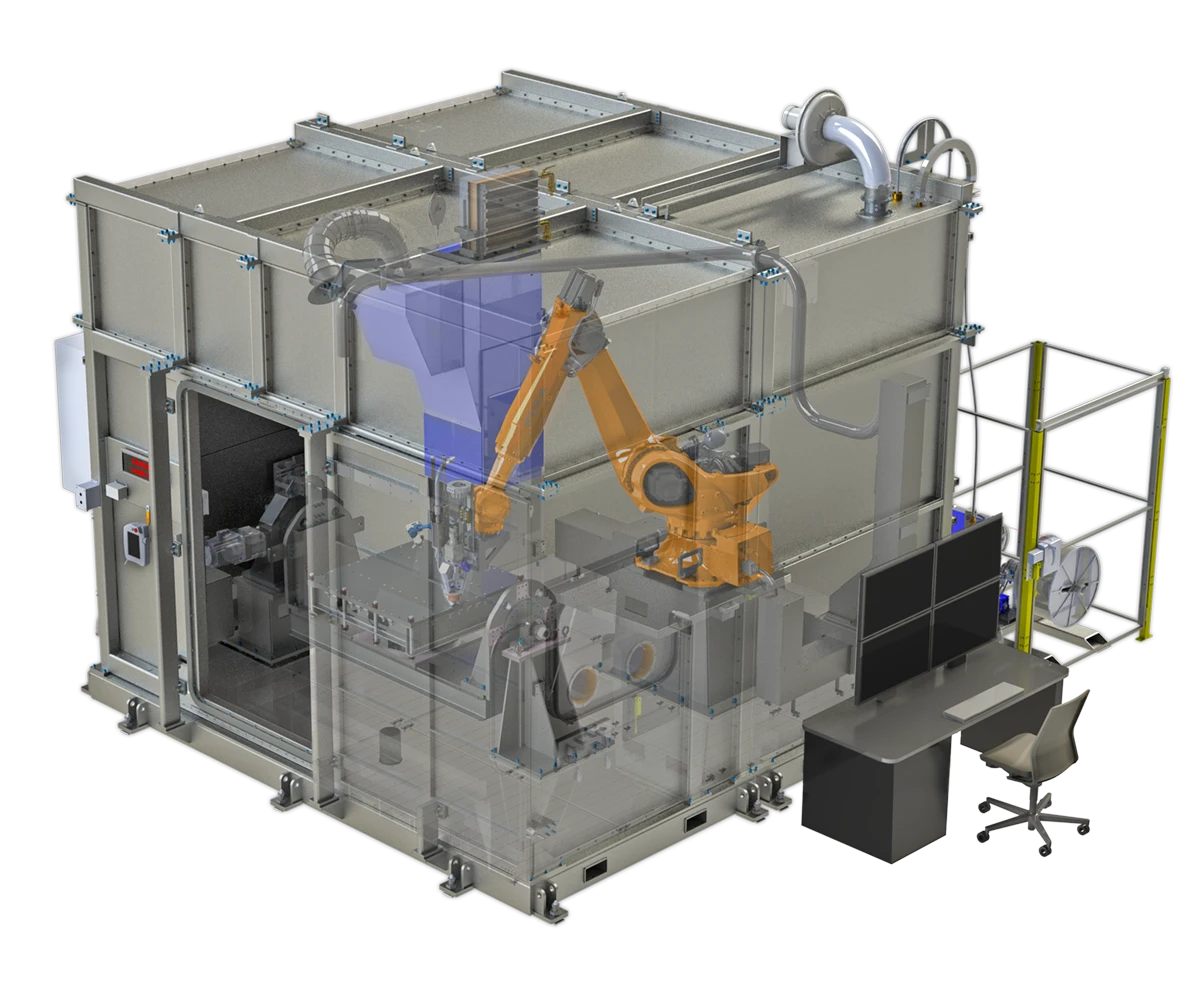
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, integrating robotic production systems into factory automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity. These systems are pivotal in enhancing productivity, ensuring consistent quality, and maintaining safety standards across various industries.
Key Benefits of Robotic Production Systems
1. Enhanced Productivity
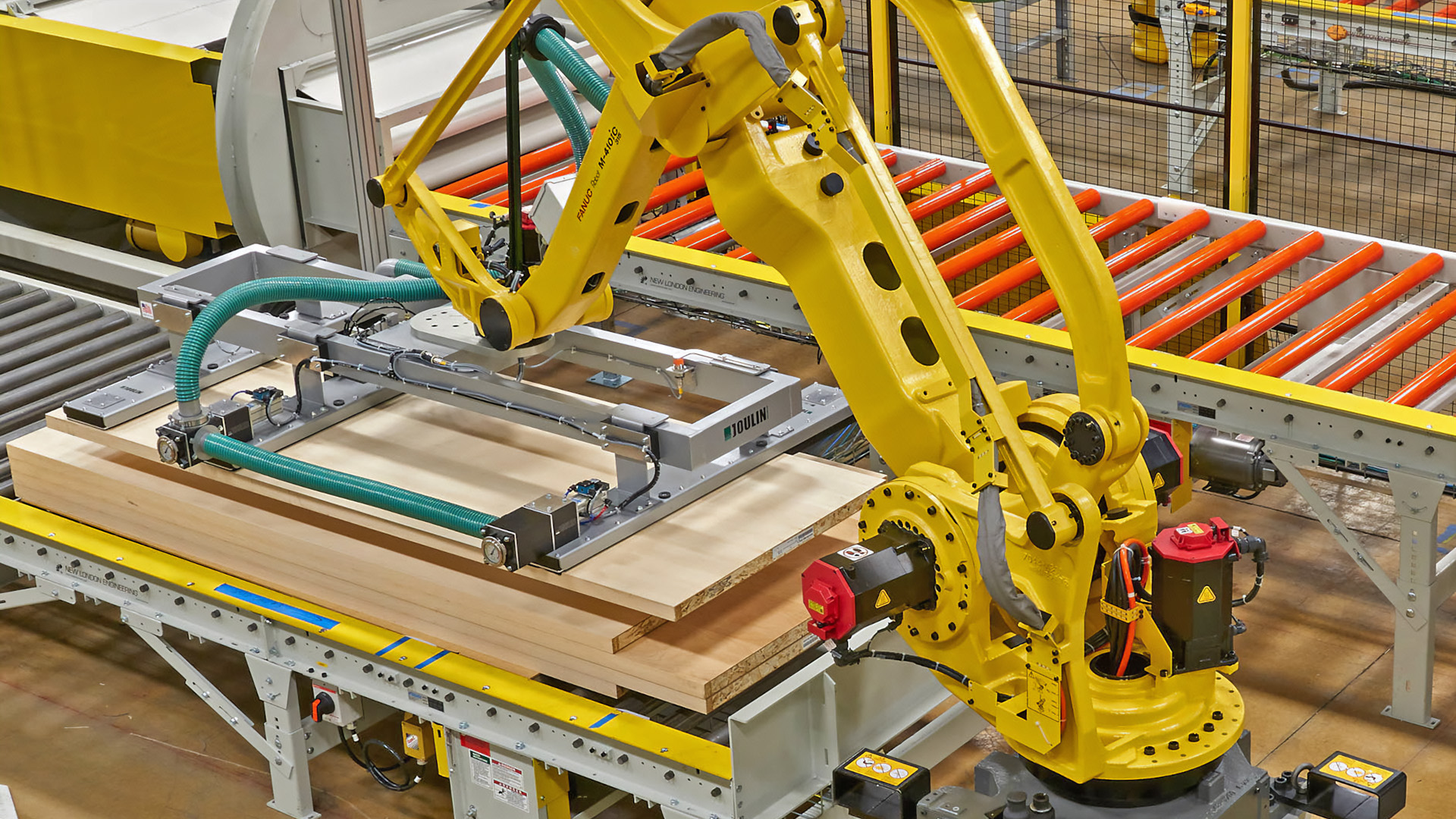
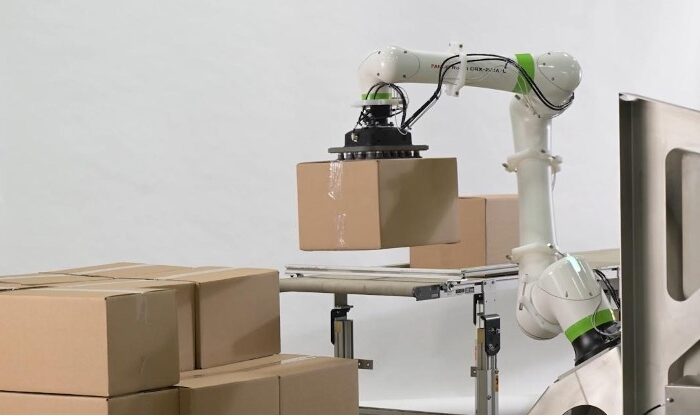
Robotic systems can operate continuously without the need for breaks, leading to significant increases in production output. For instance, automated systems can handle tasks such as welding, material handling, and palletizing with remarkable speed and precision, reducing cycle times and boosting overall throughput.
2. Consistent Quality and Precision
Robots equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems ensure high accuracy in tasks like assembly and inspection. This consistency reduces defects and rework, leading to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
3. Improved Workplace Safety
By automating hazardous tasks, robots minimize the risk of workplace injuries. For example, robots can handle heavy lifting, welding, and painting, which are traditionally associated with high injury rates.
4. Cost Reduction
While the initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, the long-term savings are significant. Robots reduce labor costs, minimize errors, and decrease downtime, leading to a favorable return on investment over time.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Modern robotic systems are adaptable to changing production needs. They can be reprogrammed to handle different tasks or products, providing manufacturers with the flexibility to scale operations efficiently.
Applications Across Industries
- Automotive Manufacturing: Robots are extensively used for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly, ensuring high precision and efficiency.
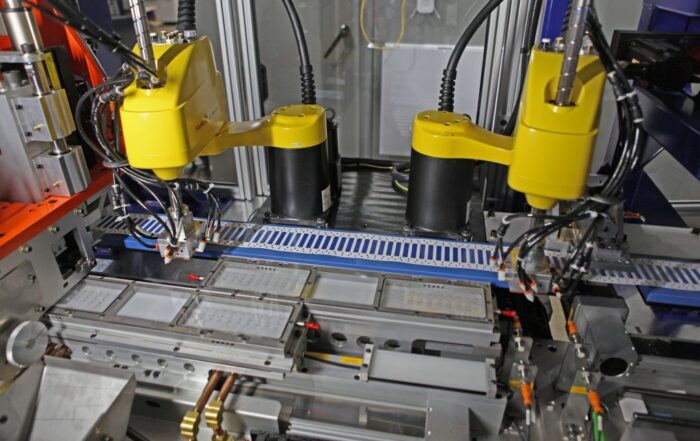
- Electronics Assembly: Pick-and-place robots are employed to assemble components onto printed circuit boards with sub-millimeter accuracy.
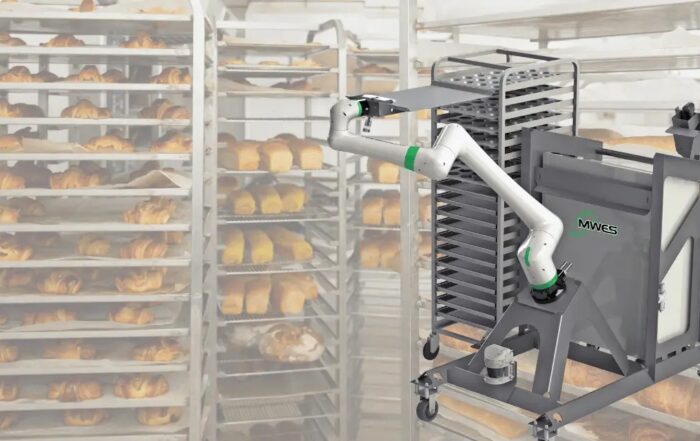
- Food and Beverage: Robotic systems handle packaging, labeling, and palletizing, improving speed and hygiene standards.
- Pharmaceuticals: Robots assist in tasks like vial filling and packaging, adhering to stringent regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
- High Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and installing robotic systems can be significant, which may be a barrier for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensuring that new robotic systems seamlessly integrate with legacy equipment and software can be complex.
- Workforce Training: Employees need to be trained to work alongside robots and manage the automated systems effectively.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of robotic systems.
Future Trends in Robotic Production Systems
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI enables robots to learn and adapt to new tasks, enhancing their capabilities and efficiency. New York Post
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity and safety in shared workspaces.
- Edge Computing: Processing data locally on robots reduces latency and allows for real-time decision-making, improving responsiveness.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Robotic systems are being developed with energy-efficient designs and materials to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
The integration of robotic production systems into factory automation is transforming manufacturing processes, offering numerous benefits such as increased productivity, consistent quality, improved safety, and cost savings. While challenges exist, advancements in technology continue to address these issues, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable manufacturing future.